"Jupiter’s upper atmosphere is composed of a neutral thermosphere and charged ionosphere. Astronomers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have spotted unexpected small-scale intensity features such as arcs, bands and spots in Jupiter’s low-latitude ionosphere in the region above the Great Red Spot.
Because Jupiter receives only 4% of the sunlight that is received on Earth, astronomers predicted this region to be homogeneous in nature.
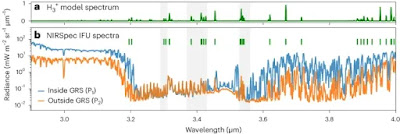
University of Leicester astronomer Henrik Melin and his colleagues observed the Great Red Spot in July 2022 using the Integral Field Unit of Webb’s Near-InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec).
Their Early Release Science observations sought to investigate if this region was in fact dull, and the region above the iconic Great Red Spot was targeted for Webb’s observations.
They were surprised to discover that the upper atmosphere hosts a variety of intricate structures, including dark arcs and bright spots, across the entire field of view.
Although the light emitted from this region is driven by sunlight, the team suggests there must be another mechanism altering the shape and structure of the upper atmosphere.
“One way in which you can change this structure is by gravity waves — similar to waves crashing on a beach, creating ripples in the sand,” Dr. Melin said."
SciNews